What is DHA? DHA is an omega-3 fatty acid that plays a huge role in overall health, especially brain optimization.
Everyone — from infants to adults — can benefit greatly from regular consumption of DHA.
Unfortunately, those eating the standard American diet don’t consume nearly enough fish to reach the recommended dosage of DHA.
And with all of the buzz around DHA’s brain-boosting benefits, companies are now rushing to include DHA into baby foods and infant formulas and adults are prioritizing supplementation to aid in managing neurological disorders like depression, Alzheimer’s disease and post-traumatic stress disorder.
This is a good thing.
So is DHA supplementation really that important? Are there negative consequences that come with DHA deficiencies?
Let’s find out.
In this article we’ll talk about:
What Exactly is DHA?
DHA, or docosahexaenoic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acid (PUFA) that plays a huge role in your brain health, especially during infancy and pregnancy.
It is a long-chain omega-3 fatty acid that is found most commonly in cold-water fish including tuna, salmon, cod liver, halibut and mackerel.
DHA is a critical component of every cell in your body and it’s required for maintenance in optimal skin, eyes and brain health. It makes up over 90% of omega-3 fatty acids in your brain and up to 25% of the brain’s total fat content[*][*][*][*].
DHA is used as a supplement for premature babies and included in baby formula to help promote mental development. This started because DHA is naturally found in breast milk.
Numerous research studies are now showing that DHA supplementation can help everyone — from infants to adults — to improve mental cognition.
How Does DHA Work in the Body?
DHA, which is mainly located in cell membranes creates gaps between cells to make them more fluid. This makes it easy for nerve cells to communicate electrical signals to each other[*].
Better nerve cell communication and fluidity helps the brain and body by:
- Increasing membrane permeability, making it more difficult for cancer cells to grow in the body.
- Regulating cellular energy through the mitochondria
- Fighting inflammation
- Lowering blood triglycerides
DHA helps extract energy from ATP (adenosine triphosphate) — the body’s main energy currency — to help prevent the damaging of nerve cells.
What Are the Best Sources of DHA?
DHA is most commonly found in fatty fish, algae and shellfish [*]:
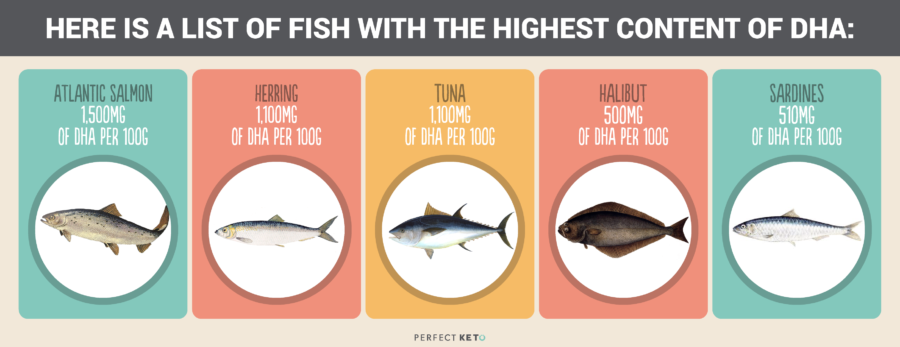
DHA is present in small amounts in meat and dairy, specifically from grass-fed animals. Fish oils such as cod liver oil can also provide up to 1,000mg of DHA in just one tablespoon.
For most people, it can be difficult to get the proper amount of DHA so taking a supplement like Keto Nootropic is a great idea.
The Role DHA Plays on the Brain
DHA is the single most abundant omega-3 fatty acid in the brain and plays a large role in brain function.
The amount of other omega-3 fatty acids such as EPA are significantly lower in the brain, typically up to 300 times lower[*].
A number of studies have shown that increased consumption of omega-3 oils can improve several neurological functions such as the reduction of Alzheimer’s disease symptoms.
It’s important to look at the EPA to DHA ratio when shopping for omega-3 oils. The ratio can vary considerably between supplements and most products have higher concentrations of EPA because it’s less expensive and has a less fishy odor than DHA.
But, studies have shown that most of the neurological benefits of omega-3 oils come from DHA instead of EPA.
DHA is Crucial During Pregnancy, Infancy and Childhood
Brain development undergoes the fastest and most complex growth during the last trimester of pregnancy and during the first two years of birth.
Since the infant brain isn’t able to convert enough alpha-linolenic oil into DHA, the baby depends completely on its mother to supply DHA[*].
There is strong evidence showing that the placenta takes up DHA from the mother to ensure proper amounts for the baby to use[*].
More than half of the energy supply during fetal development is devoted to growing the brain with DHA making up 30% of the brain and 50% of the eye structure.
It’s been shown that after birth, DHA levels can fall in babies between the ages of 6 and 12 months because once birthed, they can no longer depend on the mother for adequate DHA intake.
DHA also plays a critical role in helping grow a healthy brain after birth. It needs to compile in the CNS (central nervous system) for the brain to develop properly[*].
Babies up to the age of two need to rely on DHA more than children and adults. This is because their brains and eyes are growing rapidly. Large amounts of DHA are required to form cell membrane structures in the brain and eyes[*][*][*].
Evidence has shown that higher DHA in babies’ diets results in increased cognitive and visual functioning[*].
Conversely, a DHA deficiency in humans during the early stages of life has been linked to ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder), aggressive behavior and learning disabilities[*].
An adequate supply of DHA in the mother’s diet is crucial for normal brain development in babies.
Clearing the Mental Fog as an Adult with DHA
DHA consumption is still essential after birth and childhood. It plays a huge role in the structure and functioning of the adult brain.
While many people look at the brain as something that doesn’t change after childhood, it is constantly in a fluid state. The brain forms millions of new nerve connections, alters and replaces membrane lipids regularly.
Therefore, dietary changes like increasing DHA consumption can alter brain lipids which impacts brain functioning. That’s why DHA is a key ingredient in most nootropics.
Evidence has shown that DHA distribution in the brain changes as we get older.
In adults, the highest levels of DHA are in the cortex (responsible for cognition) and lowest in the medulla (responsible for memory). This provides enough evidence that DHA consumption is essential for maintaining sharp brain cognition.
DHA Helps the Aging Brain Stay Young
Numerous research studies have seen that decreases in DHA is associated with brain aging factors such as increased oxidative stress and DNA damage[*][*].
Studies have shown that supplementing with a DHA supplement can significantly help with improvements in verbal fluency, learning and memory for people with mild memory deficits[*][*].
Commonalities Between DHA and Brain Disease
The most common brain disease in elderly people is Alzheimer’s disease. It affects up to 10% of adults over 65.
People with Alzheimer’s disease have significantly lower levels of DHA in the neurons of the hippocampus, which is the area of the brain affected by this disease.
The hippocampus is critical for creating recent memories, also known as working memory.
Researchers have found that phospholipids, which normally contain the highest levels of DHA — are depleted in the parts of the brain that are most affected by Alzheimer’s disease[*].
Studies have seen a large correlation with older people who start showing symptoms of Alzheimer’s and a low level of DHA in the brain and liver[*][*].
Conversely, people with higher blood DHA levels have shown a reduced risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease[*].
Research studies have found up to a 60% reduction in Alzheimer’s disease in people who ate at least one meal containing fish a week[*][*].
Another study showed that DHA provided a strong protective neurological effect. This study found that the intake of alpha-linolenic acid — a plant-derived omega-3 fatty acid — was linked to a reduction in the risk of Alzheimer’s disease[*].
Not only does DHA supplementation improve memory in people with Alzheimer’s, but it has also proven to improve general age-related memory loss[*].
How DHA Positively Affects Neurotransmitters
The evidence is clear that DHA has extended benefits on helping prevent memory loss and improving brain function.
But it doesn’t stop there.
Studies have shown that omega-3 oils, specifically DHA, can also help support health neurotransmitters, which are the chemical messengers between cells.
It has been shown that DHA supplementation can help restore the neurotransmitter release in the hippocampus as well as helping reverse age-related memory recall. This is largely due to the increased fluidity between cell membranes that occurs from higher levels of DHA[*].
DHA supplementation positively affects the following neurotransmitters[*][*][*]:
- Serotonin — helps regulate mood, social behavior, appetite, sleep, memory and sexual desire.
- Norepinephrine — plays a role in the ability to concentrate and increases reaction time.
- Acetylcholine — helps sustain attention and enhances memory.
- Glutamate — responsible for sending signals between nerve cells to help with memory recall and learning.
- Dopamine — responsible for attention, motivation, mood and is associated with the “reward” centers of the brain.
DHA Helps With Depression, Anxiety and ADHD
More Americans are being diagnosed with neurological disorders like depression, anxiety and ADHD more than ever before.
Many researchers have suggested this increase to be linked with chronic brain inflammation[*].
Deficiencies in omega-3 oils are known to affect both serotonin and dopamine neurotransmitters. These transmitters along with brain inflammation play a huge role in depression and anxiety.
Fortunately, studies have shown that increased DHA supplementation can help with depression and anxiety symptoms by helping reduce excitotoxicity — the process that occurs where neurons are damaged and killed — and by decreasing brain inflammation[*].
Animal studies have also concluded that diets with DHA supplementation can counteract learning problems.
These animal studies conducted on mice showed that diets with zero DHA impaired memory and learning and that re-incorporating DHA into their diet reversed these neurological deficits[*][*].
What’s the Optimal Dosage of DHA?
The average consumption of DHA is 100mg per day[*][*].
And according to most health guidelines, the recommended dosage for healthy adults should be at least 250-500mg of combined EPA and DHA per day[*][*][*][*].
Pregnant mothers are encouraged to consume at least 200mg of DHA or 300-900mg of combined EPA and DHA per day[*].
Children up to the age of two should have around 5mg per pound of body weight while older children need up to 250mg of DHA per day.
People with mild cognitive problems or older people beginning to display symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease can benefit from a larger consumption of DHA of around 500-1,700mg of DHA per day[*][*][*][*].
DHA supplements are easily tolerated by the body and consuming larger amounts is safe. But consuming more than two grams a day does not have any increased benefits and most times your body will just excrete any excess DHA through urine[*][*].
Tip: To make DHA even more effective, several studies have concluded that pairing curcumin — a component of the spice turmeric — can significantly boost DHA levels in the brain.
Using a supplement that contains both DHA and turmeric like Keto Nootropic can increase the brain boosting benefits and help you stay mentally alert.
Turmeric helps enhance the synthesis of DHA from its precursor, alpha-linolenic acid and also elevates levels of enzymes associated with the synthesis of DHA in both liver and brain tissues[*][*].
Precautions to Consider When Supplementing with DHA
While DHA supplements are generally well tolerated even in large amounts, omega-3s are considered anti-inflammatory which can thin the blood.
Make sure to consult with your doctor before taking omega-3s if you are currently taking blood thinning medication.
DHA is a Crucial Nutrient at Every Stage of Life
The overwhelming amount of evidence around omega-3 oils, specifically DHA proves that it is one of the most important components for brain health and overall quality of life.
No matter what stage in life — from infancy to adulthood — DHA supplementation plays a huge role in brain development and upkeep for optimal cognitive function.
But the standard American diet doesn’t contain nearly enough DHA to warrant the brain boosting benefits it known for. Deficiencies in DHA are linked to neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s, depression and anxiety.
Fortunately, knowing this is half the battle.
Increasing DHA intake from supplements like Keto Nootropic can greatly improve brain disorders that may have occurred from an omega-3 oil deficiency and can even enhance cognitive function to help you focus, improve your mood and enhance memory recall.