Does a ketogenic diet also double as a healthy endocrine diet?
The endocrine system for most people remains one of those biology or anatomy chapters learned in class and never thought about again.
But others have the misfortune of developing an endocrine disorder if theirs isn’t functioning as well as it should.
This system of glands is one of the most vital in your body since it’s connected to so many important functions, including your metabolism, blood glucose regulation and reproductive success.
And all it takes is one miscommunication in this system or an imbalance of hormones to create a huge ripple effect on your overall health.
So with the help of this guide, you’ll learn:
I promise we’ll keep everything simple and easy to understand.
And that means starting with a few basic introductions and explanations.
Meet the Stars of Your Endocrine System
You may not be able to rattle off all the moving pieces that make up your endocrine system in a pop quiz, but you’ve probably heard of at least a few of them.
Basically, your endocrine system is the name given to the group of eight major glands found throughout your body.
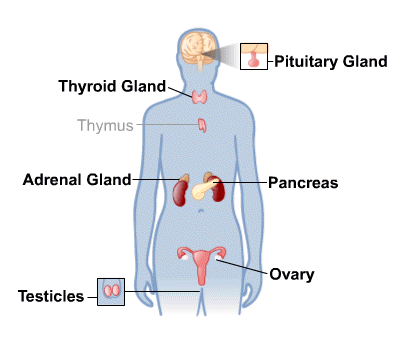
As you can see from the image above, you probably know many of these important glands, but you may not have realized they were connected to one large system including your:
- Pituitary gland
- Pineal gland
- Hypothalamus
- Thyroid gland
- Parathyroid
- Adrenal gland
- Pancreas
- Testicles (in men) and ovaries (in women)
These glands are responsible for regulating hormones, which are essentially chemical messengers your body uses to get work done, and releasing them into your bloodstream so they can initiate those different processes.
And since there are endocrine glands from your head down to your reproductive organs, they can affect your overall health and how you’re feeling.
Your endocrine system regulates several processes, such as[*][*]:
- Your growth and development
- Heart rate
- Movement
- Mood
- Metabolism
- Sexual function
- Reproduction
- Respiration
- Sensory perception
It can also affect how well you sleep, as I’ll touch on later in this guide, too.
An imbalance in how your glands function can lead to an endocrine disorder.
Which is why it’s so crucial you know what to look for.
10 Signs Your Endocrine System Isn’t Functioning Right
There are several reasons why your endocrine system may not be working optimally, including:
Your age. As you may expect, with age comes changes in your hormones and your endocrine system may have trouble adjusting for these.
But important cells can also be damaged in addition to your increasing or decreasing hormone levels over time[*].
When this happens, the chemical messages are altered and so is hormone regulation.
Genetics and stress levels can also wreak havoc on your endocrine system. In these cases, your “fight or flight” stress hormones may rise off the charts and lead to chronic mental and physical health issues[*].
And that’s not all.
Environmental endocrine disruptors (EDC) are fighting your body everyday.
These are chemicals that can leach into your bloodstream and send the wrong messages to your hormones[*].
Found in everything from plastic containers to chemical pesticides sprayed on fruits and veggies, these EDCs mimic real hormones in your body even though they don’t put in any of the real work.
EDCs trick your body into using these fake chemical messengers, and once activated, may cause a lot of health issues and damage to your system overall[*].
And you may not have a clue any of this is going on below the surface.
So how can you tell if your system is working as it should?
Answering yes to any of these questions may be a red flag yours isn’t as balanced as it should be:
- Do you have trouble sleeping?
- Are you feeling down or depressed?
- Do you suffer from low energy?
- Are you losing hair?
- Is your skin dull?
- Do you suffer from a low sex drive?
- Do you gain weight easily and struggle with weight loss?
- Have you noticed your skin seems puffier than normal?
- Do you deal with bursts of anger or fear?
- What about anxiety or trouble concentrating such as ADHD?
While there’s no way to diagnose yourself from these symptoms alone, you can schedule a visit with your primary doctor if you’re experiencing any of them to learn more about what your body may be trying to tell you.
Your doctor can run a full panel of blood work to test your hormone levels and check for any high or low imbalances.
These may be a sign something even bigger is going on, such as an endocrine disorder, which I’ll dive into next.
The Top Endocrine Disorders
When hormones go above or below the normal range, or they don’t respond or work quite as well as they should, an underlying endocrine disease could be to blame.
The most common endocrine disorder in the United States is diabetes so let’s start with this one first.
#1: Diabetes
As this guide on the topic already explains, diabetes is a disease that occurs when a person’s blood sugar levels are chronically high.
If your body doesn’t produce enough of the hormone insulin, or it struggles to use it efficiently, the excess sugar from what you eat or drink during the day is left floating around in your bloodstream instead of being filtered out like it should.
When this buildup continues to snowball, you develop type 2 diabetes, an endocrine disorder affecting 30.3 million Americans — or close to 10% of the population[*].
You can learn more about diabetes here.
Up next is PCOS, which is the number one endocrine disorder in premenopausal women.
#2: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine disorder affecting the female reproductive organs characterized by a host of symptoms and hormone levels that are anything but balanced.
This time, too much luteinizing hormone (LH) and not enough follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) throws everything else out of whack.
The chain reaction causes your body to pump out more androgens, or male sex hormones like testosterone, which then switches off ovulation.
Common PCOS symptoms include:
- Missed or irregular periods
- Infertility
- Excess hair
- Dark, velvety patches of skin
- Easily gaining weight
- Trouble losing weight
- Multiple ovarian cysts
- Anxiety, depression, fatigue and low sex drive
To learn more about PCOS, check out this guide when you’re done here.
The next set of endocrine issues affects 1% of the population[*].
#3: Thyroid Issues
The thyroid is one endocrine gland most people have heard of.
It’s a butterfly shaped gland located in your neck and it’s responsible for regulating your heartbeat and helping you burn calories for usable energy as quickly as possible.
Unfortunately, when your thyroid function is less than optimal, you’ll start feeling low in energy, have extreme sensitivities to hot or cold temperatures and may even struggle with weight issues[*].
Common medical conditions associated with your thyroid gland include[*]:
- Hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid)
- Hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid)
- Hashimoto’s disease
- Cancer
- Goiter
- Postpartum thyroiditis
Another not-so-fun fact here is that women are more likely to suffer from thyroid issues than men[*].
And these thyroid health problems can start at any time during a woman’s life, including during pregnancy and your childbearing years.
Issues with your adrenal glands can also affect your sex hormones, as you’ll see next.
#4: Adrenal Problems
Your adrenal glands, which sit just above your kidneys, produce important sex hormones and your “fight or flight” hormones like cortisol, norepinephrine and epinephrine.
These important hormones, and others found in your adrenal glands, help you[*]:
- Respond to stressful situations
- Keep your immune system strong
- Regulate blood pressure and metabolism
While Cushing’s syndrome is an endocrine disorder defined by your body producing too much cortisol, Addison’s disease occurs when there isn’t enough of it.
And chronically high cortisol levels can also lead to adrenal fatigue and diseases such as[*]:
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
- Pituitary tumors
- Pheochromocytoma, which can lead to hypertension
This next set of hormone disorders is connected to metabolism and weight gain.
#5: Hypothalamus Issues
Your hypothalamus connects your nervous system to your endocrine system and acts as the command center for signals and messages.
When certain hormones increase to specific threshold levels, the hypothalamus discharges either hormones or electrical signals from the pituitary gland[*].
The pituitary gland then replies back to the message by shutting off the valve, so to speak, once the proper amount of chemical messengers is sent out to complete the job.
If your hypothalamus isn’t functioning properly, your adrenal glands, reproductive gonads and thyroid will constantly receive the wrong messages.
With all this confusion, you can only imagine what’s happening to your hormone regulation[*].
And that’s not all these crossed wires will affect.
Hypothalamus issues, such as hypothalamic dysfunction, can throw off[*]:
- Your weight
- Appetite
- Emotions
- Growth
- Sex drive
- Sleep cycle
- Body temperature
- Salt and water balance
- Production of breast milk
There’s also one more gland to pay attention to here.
#6: Poor Pineal Gland Function
Your pineal gland, which is teeny tiny and located at the base of your brain, has a giant impact on your sleep.
This important gland helps you produce melatonin, which is a hormone that regulates your sleep cycle, or circadian rhythm.
If you’re having trouble sleeping and you know it’s not related to keto insomnia, this may be the gland you have checked first.
And if you’re experiencing any of the other symptoms we just covered, it’s smart to visit your doctor to have a full panel of bloodwork done and hopefully pinpoint which gland, if any, aren’t up to snuff.
Once you get the news, or to prevent any imbalances currently, you’ll want to follow these steps to keep your hormones in order.
Is a Ketogenic Diet a Good Endocrine Diet?
A balanced diet and regular exercise is the secret to keeping your endocrine system at its best.
And emerging research shows a diet rich in healthy fats and low in carbs, such as a ketogenic diet, has positive effects on your endocrine’s well being[*].
Researchers from three small studies on obese diabetes patients discovered a ketogenic diet[*]:
- Reduced fasting blood sugar
- Lowered insulin levels to increase insulin sensitivity
- Promoted weight loss significantly more than the low-fat control groups
Another larger body of research shows people with metabolic syndrome also saw improvements on a ketogenic diet[*].
Metabolic syndrome is the name for a cluster of health conditions like high blood pressure, insulin resistance, and high cholesterol which increase your chances of developing diabetes, heart disease and stroke.
Researchers say metabolic syndrome has a large effect on how well your hormones stay regulated and specifically mention:
“[I]ndividuals with metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance and [type 2 diabetes] are likely to see symptomatic as well as objective improvements in biomarkers of disease risk if they follow a well-formulated very-low-carbohydrate diet.”
These studies show promise for keto being used as an endocrine diet.
And when it comes to PCOS, one small study, among many, showed even better results.
After being on a keto diet for 24 weeks, women[*]:
- Lost weight (down about 12%)
- Reduced their free testosterone levels by 22%
- Improved their LH/FSH balance by 36%
- Also improved their fasting insulin (down 54%)
And two women became pregnant during the study despite struggling with infertility in the past.
Plus, as we touched on in this guide on keto and hormones, when your body produces ketones, it then uses these energy molecules to regulate and strengthen your immune system.
And that can help heal other organs and reset any other hormonal imbalances.
For instance, a ketogenic diet has also been shown to reduce the active thyroid hormone T3.
This is actually a good thing since lowered levels of this hormone help preserve important muscle mass when you start to lose both fat and weight simultaneously.
The benefits we’re seeing in these studies isn’t just from ditching sweet potatoes in favor of low-carb leafy greens; they also come about thanks to the increase in mono- and polyunsaturated fats a ketogenic diet encourages, especially the right balance of anti-inflammatory omega-3 fatty acids to omega-6s.
Plus, some of the best foods you can eat for a healthier endocrine balance are all found on the keto diet.
The Top Foods to Eat to Keep Your Endocrine System Healthy
Weave these keto-friendly foods into your weekly meal plans and you’ll help keep your hormones in balance and your system happy:
#1: Grass-Fed Beef
As mentioned in this guide on grass-fed beef, include this staple in your keto menu planning and you’ll drastically improve your blood glucose levels, which can help you prevent and treat diabetes and keep other endocrine disorders at bay.
This is in part because grass-fed beef is rich in good fats such as omega-3s, similar to salmon.
Grass-fed beef (GFB) is also loaded with vitamin B6, which can support your pineal gland by helping it regulate and produce more melatonin so you can enjoy a restful sleep.
GFB is also lower in calories and may even be able to help you ward off cancer too.
The next food group on the list delivers tons of health benefits for their small size.
#2: Specific Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds — the right kind and in the right amount — should also become a staple in your keto diet.
And when it comes to support for your endocrine health, raw Brazil nuts take the lead.
These large nuts in particular are loaded with selenium, which can help fight oxidative stress and improve cognitive function in adults.
Selenium also plays a key role in[*]:
- Changing a cell’s function
- Thyroid metabolism
- Cell growth
- Modifying cell signals
- Keeping your sperm count where it should be
Adding more selenium to the diets of lab rats helped them prevent and treat negative side effects of diabetes, including heart and kidney issues as well as blood clotting problems[*].
Brazil nuts also helped reduce serum lipid levels, triglycerides and cholesterol in human participants in another study, which are all biomarkers that can help to improve your overall health, including your endocrine system.
Seeds give you the same dose of healthy fats plus essential minerals, amino acids, vitamins and fiber, making them another great option here.
Chia seeds, flax, hemp seeds and pumpkin in particular are packed with magnesium, which can improve blood sugar and insulin resistance and trigger anti-inflammatory responses.
On top of these, the next few food groups also fight inflammation and lead to better endocrine health.
#3: Wild-Caught Seafood
Wild-caught fish such as salmon, sardines and tuna, are also bursting with healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
This powerful type of unsaturated fat can:
- Lower your risk of stroke, heart disease and heart attacks
- Reduce inflammation
- Decrease your risk of cancer
- Improve your brain healt
And guess what?
Oily fish like sardines and mackerel are also good dietary sources of vitamin D, which is actually a hormone even though it’s called a vitamin.
While you can raise your vitamin D levels with sunlight and dairy products, these fatty fish give you more nutritional bang for your buck.
All of this can ensure your body is functioning as it should, including your hormones.
You’ll also find those same omega fats in shellfish like clams and the next two foods on the list.
#4: Flaxseed, Avocado and Olive Oil
Flaxseed oil and avocado oil each contain a high amount of omega-3 fatty acids, which means you’ll score the same benefits as you would eating the seafood we just mentioned.
Avocado oil is also a rich source of beta-sitosterol, a phytosterol that helps prevent cancer cells from dividing and turning into a nightmare.
While olive oil isn’t as high in omega 3s as flaxseed or avocado, it still brings health benefits to your body in the form of a boost of antioxidants to fight free radicals and safely keep diseases away.
Finally, whole avocados, one of the biggest VIPs on a ketogenic diet, also deserves a spot on your endocrine diet shopping list.
#5: Avocados
On top of being loaded with healthy monounsaturated and saturated fats, avocados also hide a stellar dose of fiber, magnesium and potassium, which can all support your overall health.
Avocados even contain a rich source of B vitamins, such as B6, just like grass-fed beef.
And, as we touched on in this guide, avocados can help improve cardiovascular health and weight management like the other foods on this list.
Ready to Start Your Keto Endocrine Diet Today?
If after reading this guide you suspect something may be a little off with your endocrine system, don’t delay scheduling an appointment with your doctor.
By running a full panel of bloodwork, you can address any endocrine issues before they turn into something more serious.
Start adding the foods we highlighted in this guide to your diet to re-balance your hormones and prevent any endocrine disorders from creeping up in your future.
A healthy diet like keto shows great potential for ensuring your hormones stay balanced and in working order.
Next, check out this guide on everything you need to know to start a ketogenic diet today.